
Introduction
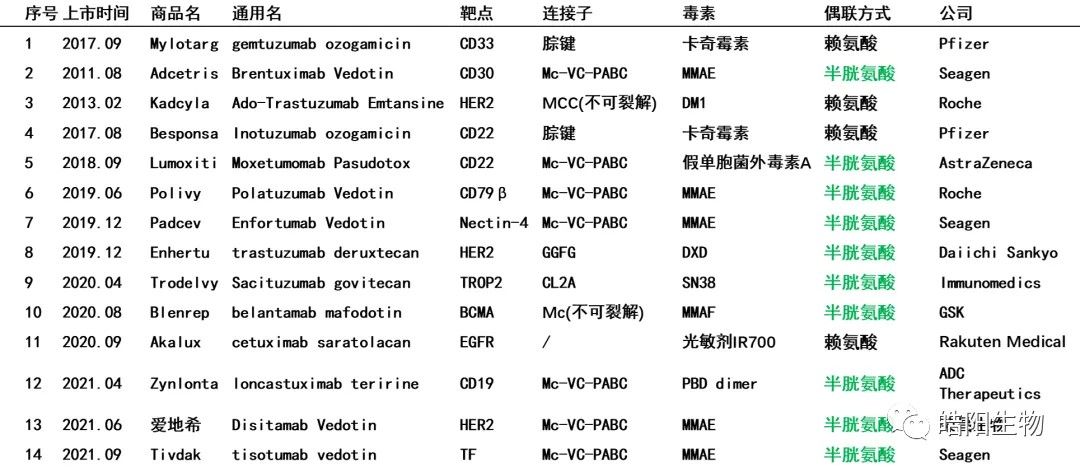
71% of currently marketed ADCs use interchain disulfide bonds for conjugation, (see the table below), which shows the importance of disulfide bonds. Today, we share with you the structure of antibody disulfide bonds, ADCs conjugated based on partially-reduced disulfide bonds, ADCs conjugated based on fully-reduced disulfide bonds, ADCs conjugated based on disulfide bridging, as well as consistency of ADCs’ DAR values.
71% Commercialized ADC Adopts Interchain Disulfide Bond coupling
01
Structure of the antibody disulfide bonds
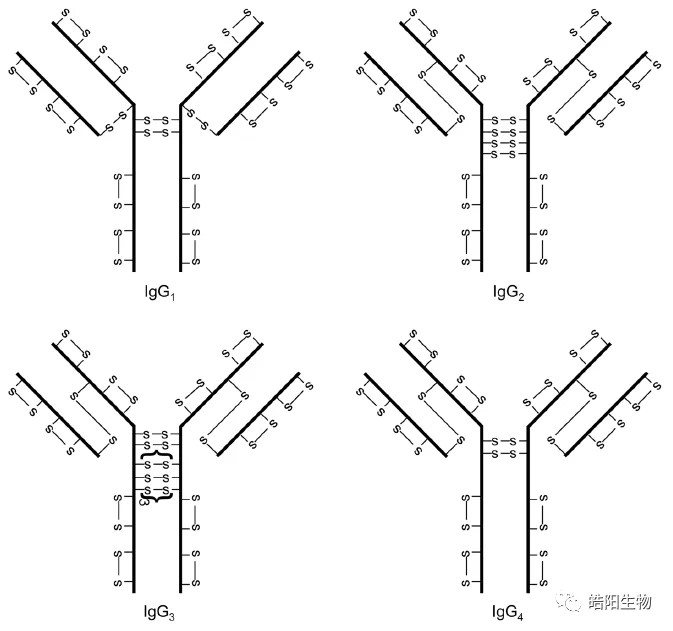
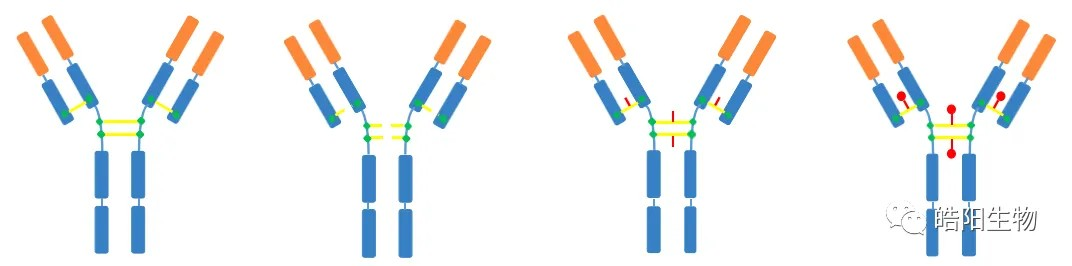
The structures of disulfide bonds in four different types of antibodies are shown in the figure below, in which IgG1 is most widely used in ADCs. Its structure is divided into two heavy chains and two light chains, which are connected by four disulfide bonds. There are disulfide bonds on the light and heavy chains which are hardly to be reduced, so that the interchain disulfide bonds are preferentially reduced, which then conjugated to small molecule toxins through the addition reaction of maleimide and hydrosulfide groups.
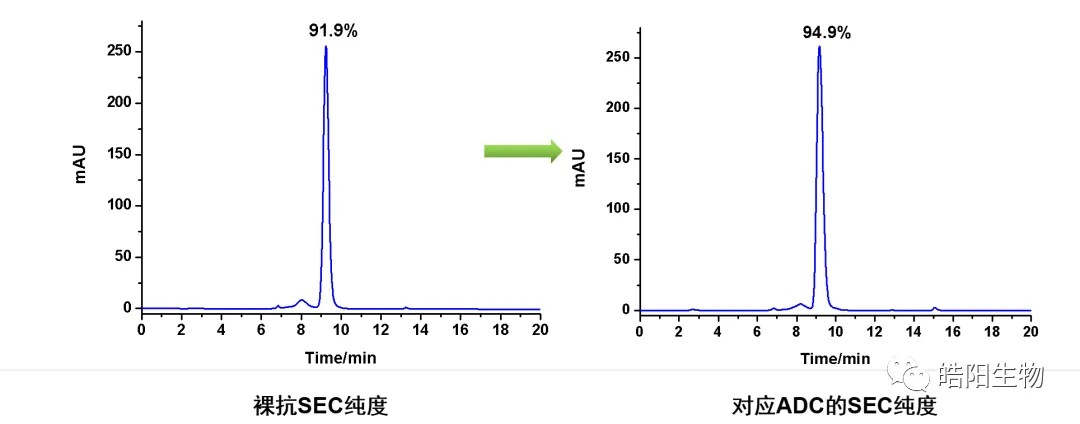
The disulfide bonds of antibodies may be mismatched in the process of re-formation. For example, in the figure below, the purity of the naked antibodies is 91.9%, and in the process of producing the ADC, it is necessary to use a reducing agent to reduce their disulfide bonds, and the final purity of the ADC reaches 94.9%. The possible reason is that the disulfide bonds between the aggregates are reduced by the reducing agent, thus leading to an increase in purity.
02
ADC based on partially-reduced disulfide bonds
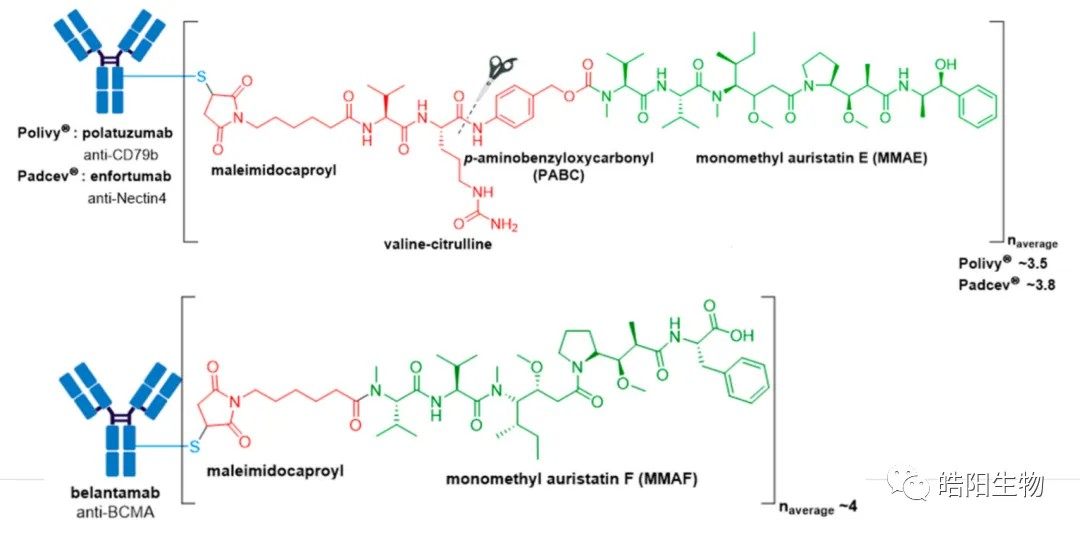
In the figure below, ADCs based on partially-reduced disulfide bonds are shown with DAR values of 3.5, 3.8, and 4.0, whereas all 4 disulfide bonds of IgG1 are reduced to 8 hydrosulfide groups. This requires changing the conditions of the reduction reaction to reduce part of the disulfide bonds. The amount of reducing agent added is usually adjusted to control the amount of reduced hydrosulfide groups, which in turn regulates the final DAR value.
Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) is used in the reduction of disulfide bonds in antibodies due to its mild reaction conditions, excellent water solubility, and no odor, etc. The diagram below shows a reduction reaction.
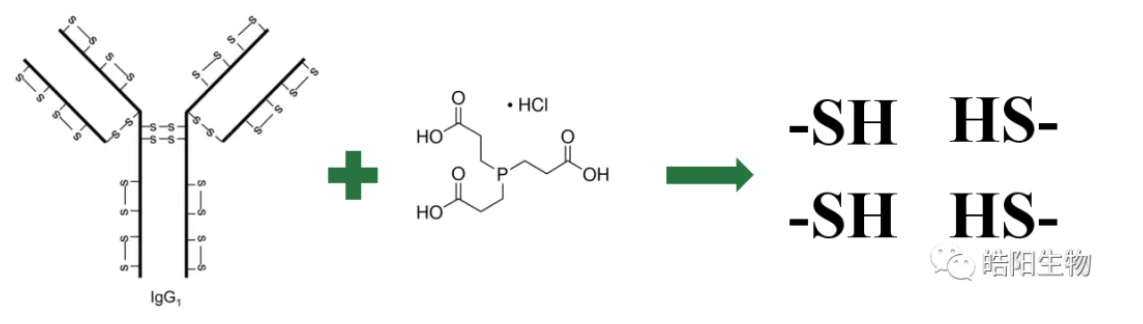
During ADC preparation, the degree of reduction of interchain disulfide bonds can be observed by SDS-PAGE. The bands are shown in the following figure, in which M is the standard protein, R is the reduced sample, NR is the non-reduced sample, H is the heavy chain, and L is the light chain. The conjugation is carried out by reducing the hydrosulfide groups of the broken disulfide bonds, so different bands appear in the gel graph. This can be illustrated by comparing the gels of ADCs with DAR 4 and DAR 8, and it can be seen that the ADC of DAR 4 has its four interchain disulfide bonds partially broken, whereas DAR 8 has them fully broken, so the bands are differently occupied.
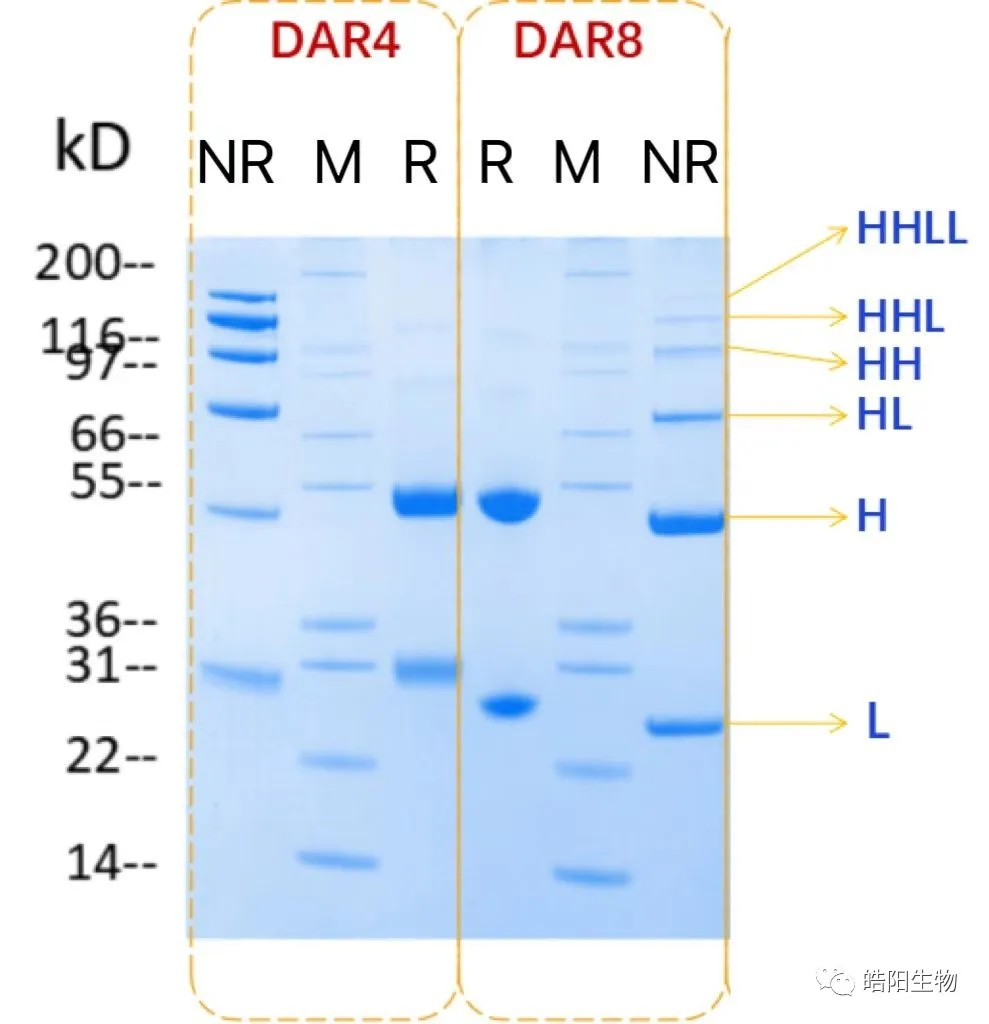
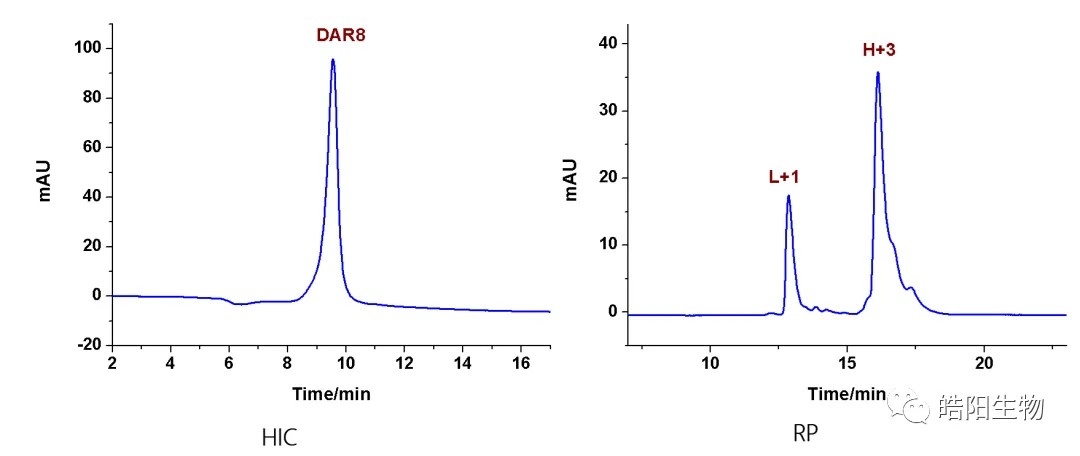
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is usually used to analyze the DAR value. Drug 0-drug 8 mean that 0 to 8 small molecule drugs are attached to the antibody, respectively. The figure is the hydrophobic interaction chromatogram of ADC samples prepared by antibody Herceptin conjugated with MMAE, with a DAR value of 4.04. For samples that cannot be analyzed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography, such as drug 0-drug 8 with indistinguishable peaks, reversed-phase liquid chromatography can be used to make a judgment, with L representing the light chain, H representing the heavy chain, and +1, +2, and +3 representing one to three small molecule drugs attached, respectively.
03
ADCs conjugated based on fully-reduced disulfide bonds
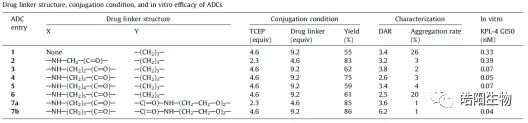
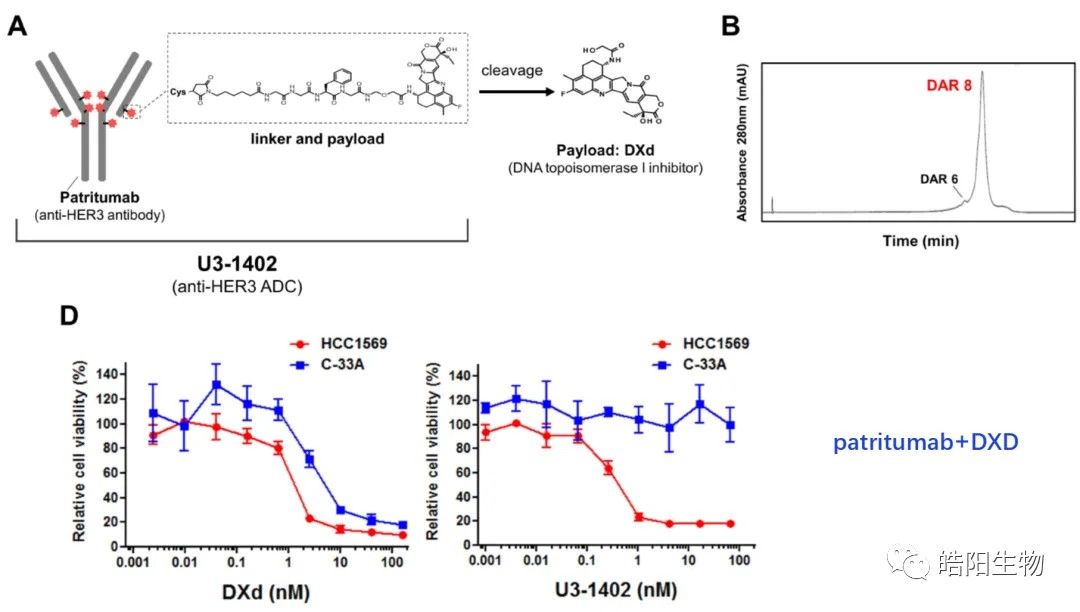
By reduction of all 4 interchain disulfide bonds of IgG1 antibody, 8 hydrosulfide groups are obtained, which can be combined with 8 small molecules with maleimide functional groups to obtain ADCs with DAR value of 8. For example, as shown in the following figure and table, when conjugating Exatecan derivatives to antibodies by different linkers, functional groups changes affect the ADC’s purity and DAR value. The best structure like deruxtecan is screened out, and its DAR value characterization chromatography shows that there is only one DAR 8 peak in the hydrophobic chromatogram, while one and three small molecules are attached to the light and heavy chains in the reversed-phase chromatogram, respectively. Again, based on this small molecule, U3-1402 is obtained by replacing the antibody with different targets.
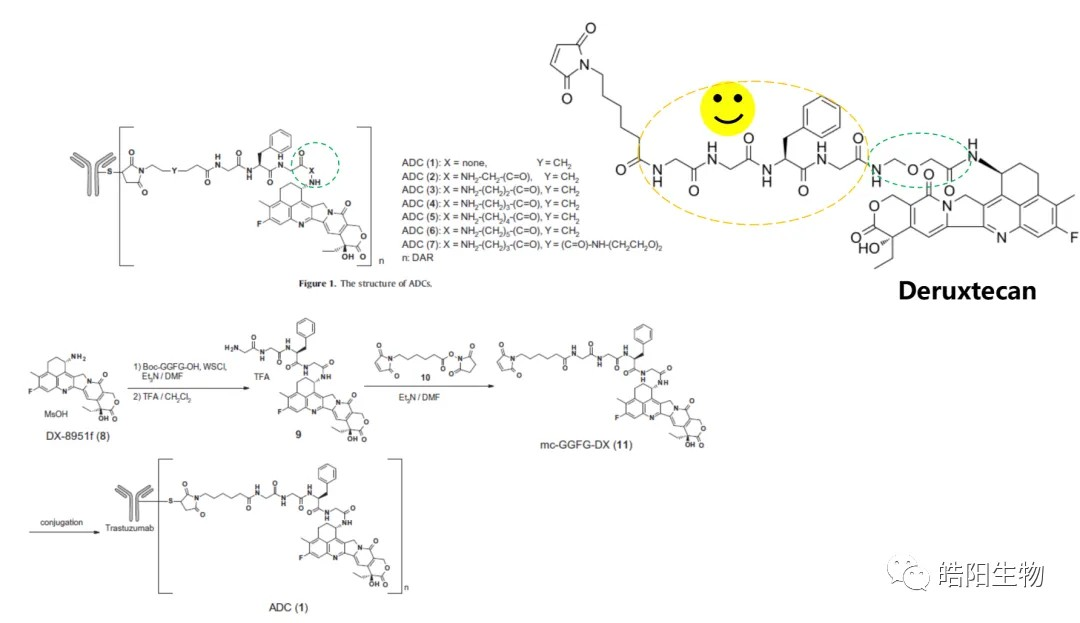
04
ADC based on disulfide bridging
Other products such as drug2, drug6, drug8, etc. are formed when producing ADCs of DAR 4. After antibody reduction, the bridging reattaches the four broken disulfide bonds by using a reagent with bifunctional groups that can react with hydrosulfide groups, but a third functional group is introduced on the linker, which can be chemically covalently bound to the functional group attached to the toxin. The adoption of this approach to DAR 4 content can be increased by more than 30%.
Conjugating MMAE with Divinylpyrimidine as a bridging reagent significantly increases the DAR 4 component as can be seen in the figure below. However, this method has a disadvantage that the two hydrosulfide groups on the same heavy chain can bridge, as shown in the gel diagram. Moreover, this reaction requires copper ion catalysis, and the amount of toxin is large, up to 40 times larger than the amount of toxin required for conjugation by maleimide functional groups.
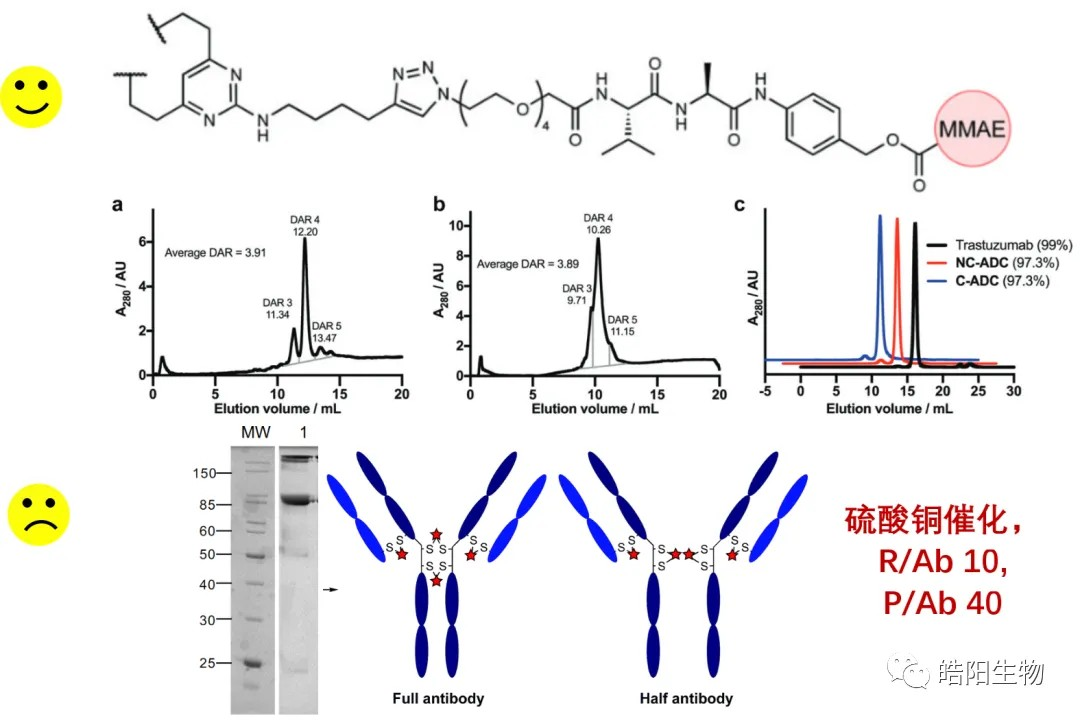
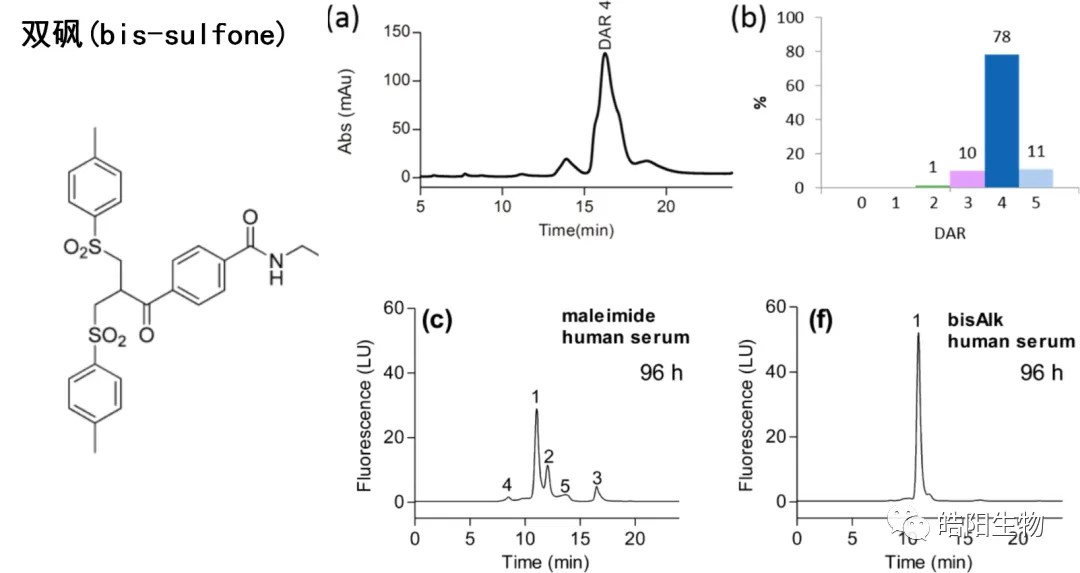
In the scheme below, bis-sulfone is used as a bridging reagent to produce ADCs of DAR 4, of which the DAR 4 component accounts for 78%, while the ADCs prepared by this process have good stability in blood.
05
Consistency and trends of ADC DAR value
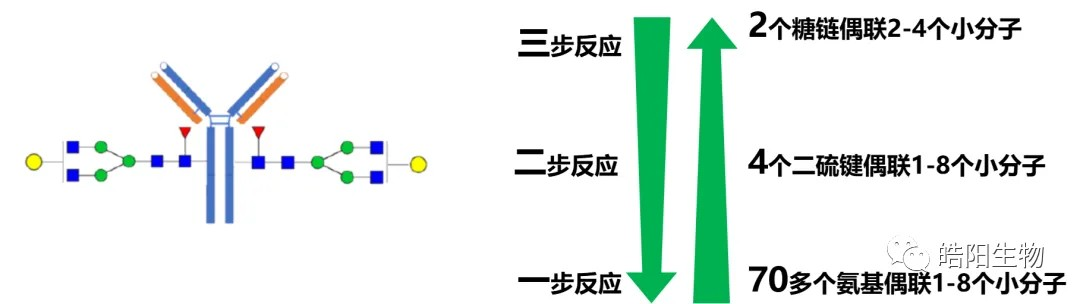
The regulatory tendency of DAR values can be summarized in the figure below, from the beginning when over 70 amino groups conjugated 1-8 small molecules, i.e. Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), to 4 disulfide bonds conjugating 1-8 small molecules, to the current 2 glycan chains conjugating 2-4 small molecules. The complexity of conjugation reactions increases with the reduction of conjugation sites
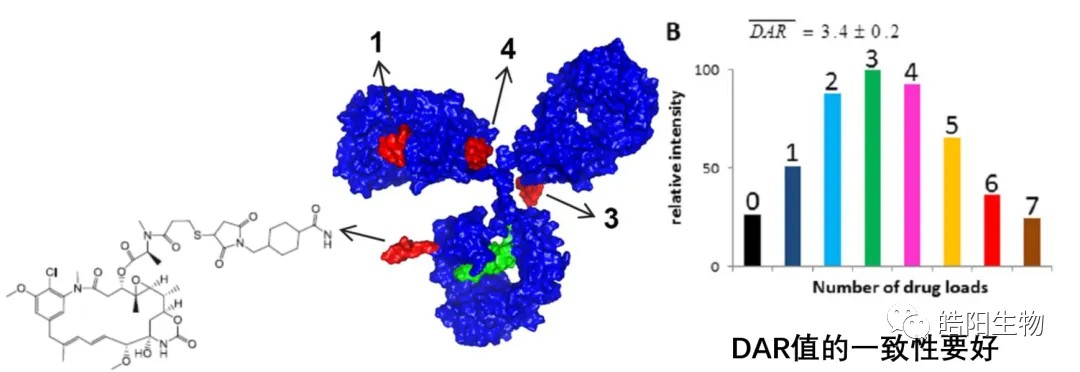
Summary
Three conjugation techniques based on antibody hydrosulfide groups are shared today, two of which belong to fixed-site techniques. The essence of the process to conjugate ADCs based on hydrosulfide groups of partially reduced disulfide bonds is to adjust the amount of reductant to control the final DAR value, and the process is matured.
8 hydrosulfide groups obtained by reducing all 4 interchain disulfide bonds of IgG1 antibody are bound to a small molecule with maleimide functional groups to obtain an ADC with DAR values of 7-8. Compared to the previous one, this conjugation technique is able to obtain ADCs with a relatively homogeneous DAR value component. The second fixed-site conjugation technique is bridging, with which the DAR 4 content can be increased by more than 30%, but the cost will grow as the chemical reaction steps increase in comparison with other hydrosulfide groups conjugations. Taking the above three techniques into consideration, we can foresee the development trend of conjugation techniques. The development trend of DAR value regulation pointed out in Part 5 shows that as the conjugation sites become more defined, the corresponding chemical reactions involved will be more complex, and the control level will be higher.
Reference
Hongcheng Liu, Kimberly May, Disulfide bond structures of IgG molecules, mAbs, 2012,4,17-23.
James McNulty, Venkatesan Krishnamoorthy, Dino Amoroso et.al, Tris(3-hydroxypropyl)phosphine (THPP): A mild, air-stable reagent for the rapid, reductive cleavage of small-molecule disulfides, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2015, 25,4114–4117.
Takashi Nakada, Takeshi Masuda, Hiroyuki Naito et.al, Novel antibody drug conjugates containing exatecan derivative-based cytotoxic payloads, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, Bioorg Med Chem Lett., 2016,26,1542-1545.
Abigail R. Hanby, Stephen J. Walsh, Andrew J. Counsell et.al, Antibody dual-functionalisation enabled through a modular divinylpyrimidine disulfide rebridging strategy, Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 9401.
Yuuri Hashimoto, Kumiko Koyama, Yasuki Kamai et.al, A novel HER3-targeting antibody-Drug conjugate, U3-1402, exhibits potent therapeutic efficacy through the delivery of cytotoxic payload by efficient internalization, Clin Cancer Res. 2019,25,7151-7161.